Heel Pitch とは、着地による鉛直方向の反発力をいかに素早く処理し、推進力に変えるフェーズに短時間で移れているかを測定したものです。この移行動作が効率的に行われていれば、スコア値は小さくなります。
| Heel Pitch はLEOMO独自の Motion Performance Indicator (MPI) の一つです。LEOMOの製品でのみ、計測することができます。 |
簡単に言うと
-
着地直後のテクニック。瞬間的に着地衝撃を吸収出来るかどうか。小さい方が上手い。
-
「着地」してから「足がフラットに地面について次に動き始めるまで」の時間が、ストライド全体の時間に占める割合。
-
スコアが悪いと、着地時にワンテンポ遅れていたり、沈んでいるように見える。
なぜ Heel Pitch が重要なのか
着地直後はどれだけテクニックがあるランナーでも着地点は体の重心よりも前であることがほとんどです。Strike ARによって評価された推進力を地面に効率的に伝えるためには、着地によって発生する鉛直方向のエネルギーを素早く処理し、できるだけ推進力を伝える加速フェーズに移る必要があります。
上の図は着地の様子を時間軸と共に表しています。
Heel Pitch は、立脚期に足がフラットになった状態(Flat State)を終えて素早く次の推進力を伝えるフェーズ(Acceleration Phase)に移行できているかを評価します。力の出し方で言えばエキセントリック収縮からコンセントリック収縮に変わるまでの時間、すなわち上の図で示す「Heel Pitch」の時間が短い方が優れています。上記の図はかかと着地の例ですが、ミッドフット着地の選手はFlat Stateまでの時間(Move to flat)も短くなるでしょう。
Heel Pitch のスコアが悪いと、着地エネルギーの処理に時間がかかっている証拠です。一般的に「遅れている」「沈んでいる」「バネ感がない」などと評価される場合が多いでしょう。
Heel Pitchは上記の時間をストライド全体に占める割合で表しています。この値は一般的な Ground Contact Time (GCT) よりも正確に推進効率を測定でき、ランナーのテクニックを表す指標となります。
Heel Pitchはスピード、疲労、シューズの種類、表面の状態によって少なからず影響を受けることがあるので、その点に気をつけながら活用すべきです。とはいえ、大きな傾向としてアスリートの特徴を表すことができるでしょう。
Heel Pitchの値について
-
単位は%(0〜100)。全体の時間に占める移行時間の割合なので0%未満になることもなく、100%より大きくなることもありません。
-
トップレベルのアスリートは30%未満の値を出すことができます
-
低い値(低い割合)ということは、立脚期における着地エネルギーを処理するための無駄な伸縮運動が少なく、素早く次のフェーズに移ることができていると言えるでしょう。
-
すなわち低い値はより効率の良い走りができていると言えます。
|
Heel Pitch |
競技レベル |
見た目による差(参考) |
|---|---|---|
|
Less than 25% |
Top-level athletes |
バネ感のある走り |
|
25–29% |
Amateur runners |
十分剛性感がある |
|
29-33% |
Casual runners |
走れているがワンテンポ遅れる |
|
More than 33% |
Not good |
沈み込んでいる、着地が遅い |
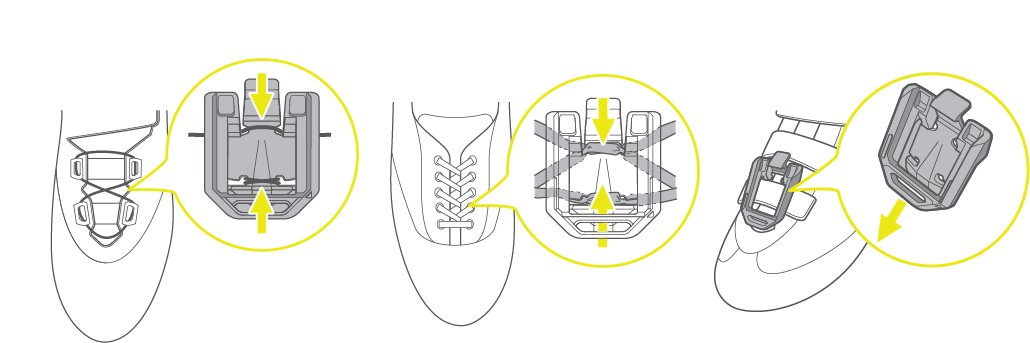
センサーの位置
- 靴の足の甲の部分に取り付けます。
-
センサークリップを使って下さい。
-
脱落防止のため、手前(足首)から奥(つま先)に差し込むように、シューズの紐やワイヤーなどにしっかりと固定して下さい。
- センサークリップをつま先近くに装着すると足の指に当たる場合があります。クリップをできるだけ足首に近い位置に装着することを推奨します。
リアルタイムデータ解析
Heel Pitch はアクティビティ中にリアルタイムで見ることが出来ます。
また、コーチは LEOMO LVS でMPIと動画を重ね合わせて記録し、見ることができます。
関連項目
Stride Cycleの一つです。同じく構成要素となるMPIであるRecoil AR、Thigh Swing Speed、Strike ARも参照して下さい。

コメント
0件のコメント
サインインしてコメントを残してください。